The NOMIS Center’s Neuroimmunology Initiative
REGISTRATION NOW OPEN
 SUMMARY
SUMMARY
Crosstalk between the immune and nervous systems— and the role this intersection plays in health and disease—has long been understudied. Now, Salk Institute scientists are at the forefront of this emerging interdisciplinary field. They are paving the way toward innovative therapeutic interventions for a wide range of disorders long thought to result from a combination of damage to the nervous system and resulting inflammation, such as Alzheimer’s disease, long COVID, and some forms of cancer.
THE CHALLENGE
The nervous system and the immune system have historically been studied in siloes. However, we know from many diseases that the interplay between the two is critical. For example, increasing evidence indicates that inflammation is associated with neurodegeneration in aging, and that a person’s brain function and mental state can affect immunity.
Yet the cells, molecules, and mechanisms that guide these connections are mostly unknown. To better prevent and treat diseases, we need to better understand at all levels how they develop and progress.
THE SALK APPROACH
The Salk Institute’s robust foundation in neuroscience and immunology presents a fertile ground for pioneering discoveries in mental health, behavior, aging, and chronic diseases that span pathogen-induced conditions, neurodegeneration, and cancer.
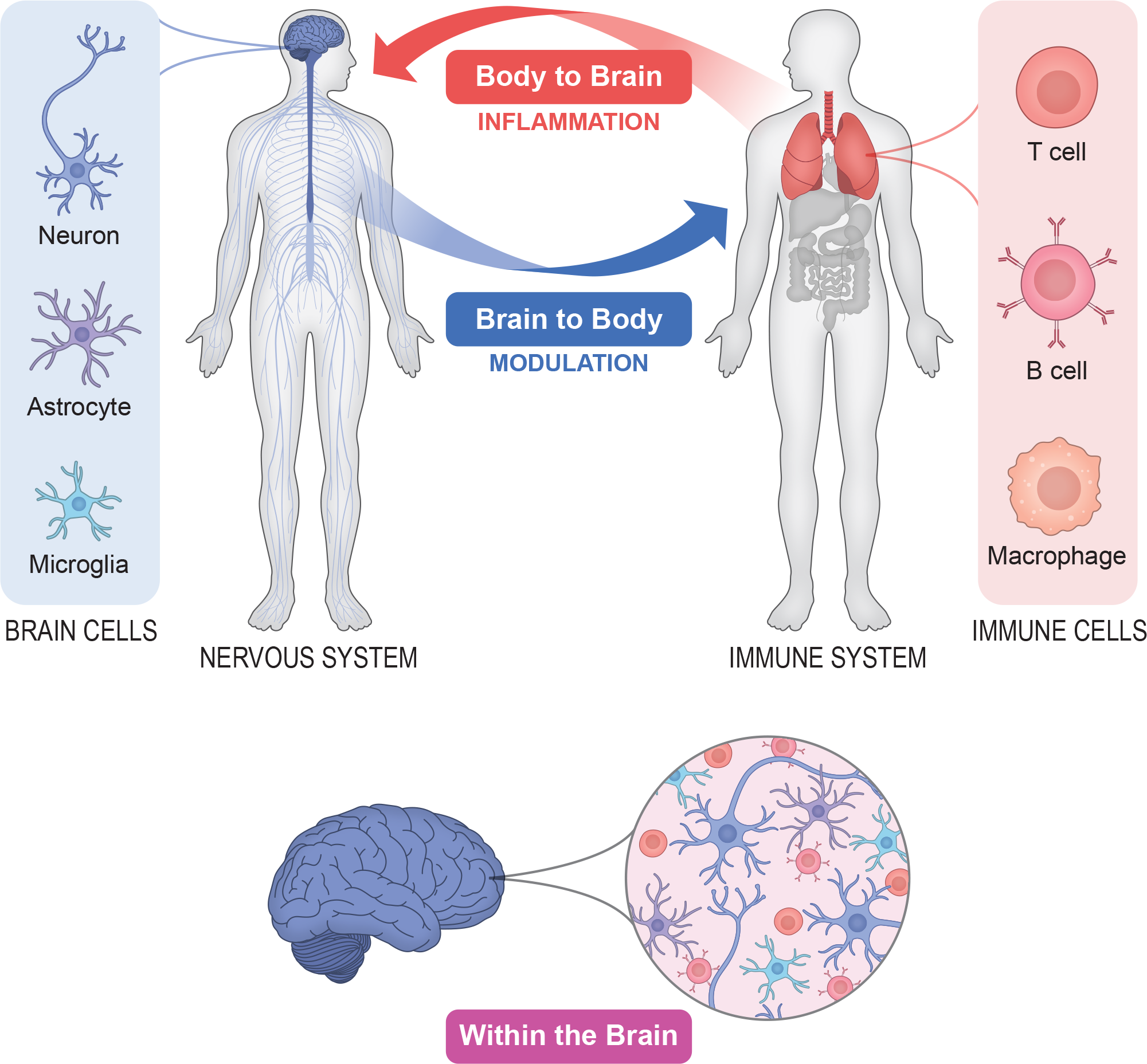
Now, thanks to a generous gift from the NOMIS Foundation, the Salk Institute has launched a new Neuroimmunology Initiative as part of Salk’s NOMIS Center for Immunobiology and Microbial Pathogenesis. Within this Initiative, Salk scientists are working to develop a deep understanding of the crosstalk between the immune and nervous systems and the role it plays in health and disease. The Neuroimmunology Initiative encompasses three interconnected research programs:
- Body to Brain: How the immune system and inflammation affect the nervous system—for example, how infection and the resulting immune response can affect brain function.
- Within the Brain: Where brain resident cells, such as microglia and astrocytes, contribute to chronic inflammation and immune cells establish long-term residence after infection—for example, chronic inflammation contributes to neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
- Brain to Body: How the nervous system modulates immune responses throughout the body—for example, we have long known that chronic stress and depression are associated with a suppressed immune system, but we don’t know why.
WHY THIS RESEARCH IS CRITICAL
The Neuroimmunology Initiative gives scientists the freedom to tackle currently unaddressed scientific questions, which will open fundamentally new areas of scientific inquiry across human health and disease. Ultimately, this work paves the way toward innovative therapeutic interventions for a wide range of disorders that have both a neurological and immunological component, such as Alzheimer’s disease, long COVID, and some forms of cancer.
HOW YOU CAN HELP
This critical research relies on philanthropic
investment to acquire cutting-edge technologies,
recruit faculty, and support trainees. To help advance Salk’s Neuroimmunology Initiative, please contact Dacia Samilo at dsamilo@salk.edu or (858) 453-4100 x2068.
