Central Resources for Information about Williams Syndrome
Williams Syndrome Association for Families, a great resource for understanding Williams Syndrome for Parents, Teachers, Clinicians, and Researchers
Williams syndrome shows gene behavior links: Key to autism? (2011) CBS News [ link to pdf ]

Documentary Film Josie: A Story About Williams Syndrome, Vision Project [ link to video ]
Williams Syndrome Oliver Sacks and UB “A highly musical species” [ link to video ]
Growing Up Different, Scientific American Frontiers [ link to video ]
A Very Special Brain, 60 minutes [ link to video ]
Williams Syndrome Demo [ link to video ]
Odd Disorder of the Brain May Offer New Clues (1994). The New York Times [ Link to article ]
Lenhoff, H.M., Wang, P.P., Greenberg, F., & Bellugi, U. (1997). Williams syndrome and the brain. Scientific American. [ Link to article ]
The Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience special Supplement “Journey from Cognition to Brain to Gene”
From Michael S. Gazzaniga, Editor-in-Chief for the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, to introduce the first supplement ever to the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, “We are fortunate to have the opportunity to publish a special issue of JOCN on Williams Syndrome. This is one of the few cognitive disorders that can be analyzed at many levels. From the genome into the study of language, this fascinating disease illuminates how brains and mind are related. Dr. Ursula Bellugi and her colleagues have performed a major service by organizing and orchestrating this special issue.”
~Michael S. Gazzaniga
Bellugi, U., St. George, M. (2000). Preface to the Journal Issue. In U. Bellugi Bellugi & M. St. George, M. (Eds.) Special issue: Linking Cognitive Neuroscience and Molecular Genetics: New Perspectives from Williams Syndrome
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(1), 1-6.
Click here to read the entire preface
I. Bellugi, U., Lichtenberger, L., Jones, W., Lai, Z., & St. George, M. (2000). The neurocognitive profile of Williams Syndrome: A complex pattern of strengths and weaknesses. In U. Bellugi & M. St. George, M. (Eds.) Special Issue: Linking Cognitive Neuroscience and Molecular Genetics: New Perspectives from Williams Syndrome
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(1), 7-29. (PMID: 10953231)
PubMed
II. Jones, W., Bellugi, U., Lai, Z., Chiles, M., Reilly, J., Lincoln, A., & Adolphs, R. (2000). Hypersociability in Williams Syndrome. In U. Bellugi.& M. St. George, M. (Eds.) Special Issue: Linking Cognitive Neuroscience and Molecular Genetics: New Perspectives from Williams Syndrome
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(1), 30-46. (PMID: 10953232)
PubMed
III. Mills, D.L., Alvarez, T.D., St. George, M., Appelbaum, L.G, Bellugi, U., & Neville, H. (2000). Electrophysiological studies of face processing in Williams Syndrome. In U. Bellugi & M. St. George, M. (Eds.) Special Issue: Linking Cognitive Neuroscience and Molecular Genetics: New Perspectives from Williams Syndrome
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, (1)12, 47-64. (PMID: 10953233)
PubMed
IV. Reiss, A., Eliez, S., Schmitt, J. E., Strous, E., Lai, Z., Jones, W., & Bellugi, U. (2000). Neuroanatomy of Williams Syndrome: A high-resolution MRI study. In U. Bellugi.& M. St. George, M. (Eds.) Special Issue: Linking Cognitive Neuroscience and Molecular Genetics: New Perspectives from Williams Syndrome
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(1), 65-73. (PMID: 10953234)
PubMed
V. Galaburda, A., & Bellugi, U. (2000). Multi-Level analysis of cortical neuroanatomy in Williams Syndrome. In U. Bellugi.& M. St. George, M. (Eds.) Special Issue: Linking Cognitive Neuroscience and Molecular Genetics: New Perspectives from Williams Syndrome
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(1), 74-88. (PMID: 10953235)
PubMed
VI. Korenberg, J., Chen, X-N., Hirota, H., Lai, Z., Bellugi, U., Burian, D., Roe, B., & Matsoka, R. (2000). Genome structure and cognitive map of Williams Syndrome. In U. Bellugi.& M. St. George, M. (Eds.) Special Issue: Linking Cognitive Neuroscience and Molecular Genetics: New Perspectives from Williams Syndrome
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(1), 89-107. (PMID: 10953236)
PubMed
Selected Background Papers from PPG
***Chailangkarn, T., Hrvoj-Mihic, B., Yu, D.X., Brown, T.T., Marchetto, M.C.N., Bardy, C., & Muotri, A.R. (2016). A human neurodevelopmental model for Williams syndrome. Nature, 536, 338-343. PubMed
Lew, C., Brown, C., Bellugi, U., & Semendeferi, K. (2016). Neuron density is decreased in the prefrontal cortex in Williams syndrome. Autism Research, doi:10.1002/aur.1677. PubMed
Järvinen, A., Korenberg, J. R., & Bellugi, U. (2013). The social phenotype of Williams syndrome. Current opinion in neurobiology, 23(3):414-22. PubMed
Mills, D. L., Dai, L., Fishman, I., Yam, A., Appelbaum, L. G., St. George, M., … & Korenberg, J. R. (2013). Genetic Mapping of Brain Plasticity Across Development in Williams Syndrome: ERP Markers of Face and Language Processing. Developmental neuropsychology, 38(8), 613-642. PubMed
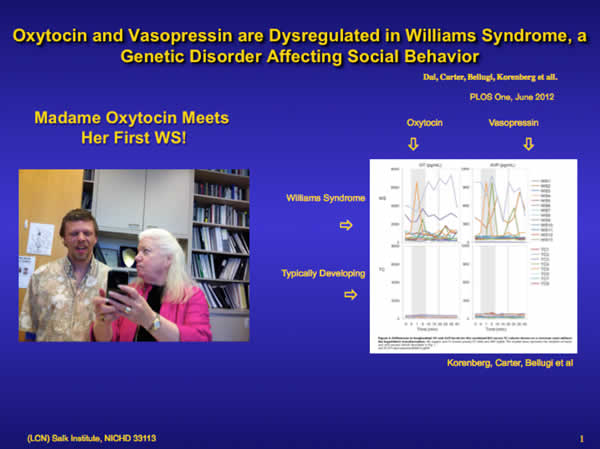
Dai, L., Carter, C. S., Ying, J., Bellugi, U., Pournajafi-Nazarloo, H., & Korenberg, J. R. (2012). Oxytocin and vasopressin are dysregulated in Williams syndrome, a genetic disorder affecting social behavior. PloS one, 7(6). PubMed
Fishman, I., Yam, A., Bellugi, U., Lincoln, A., & Mills, D. (2011). Contrasting patterns of language-associated brain activity in autism and Williams syndrome. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 6(5), 630-638. PubMed
Golarai, G., Hong, S., Haas, B., Galaburda, A.M., Mills, D., Bellugi, U., Grill-Spector, K., & Reiss, A.L. (2010). The fusiform face area is enlarged in Williams syndrome. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(19), 6700-12. PubMed
Haas, B.W., Hoeft, F., Searcy, Y.M., Mills, D., Bellugi, U., & Reiss, A. (2010). Individual differences in social behavior predict amygdala response to fearful facial expressions in Williams syndrome. Neuropsychologia, 48(5), 1283-8. PubMed
Zitzer-Comfort, C., Reilly, J.S., Korenberg, J.R., & Bellugi, U. (2010). We are social—Therefore we are: The interplay of mind, culture and genetics in Williams syndrome. In C.M. Worthman, P. Plotsky, D. Schechter, & C. Cumming (Eds.) Formative experiences: The interaction of caregiving, culture, and developmental psychobiology. Cambridge University Press (pp.133-163).
Dai, L., Bellugi, U., Chen, X.N., Pulst-Korenbeg, A.M., Järvinen-Pasley, A., Tirosh-Wagner, T., Eis, P.S., Graham, J., Mills, D., Searcy, Y., & Korenberg, J.R. (2009). Is it Williams syndrome? GTF2IRD1 implicated in visual-spatial construction and GTF2I in sociability revealed by high resolution arrays. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 149A(3), 302-314. PubMed
Haas, B.W., Mills, D., Yam, A., Hoeft, F., Bellugi, U., & Reiss, A. (2009). Genetic influences on sociability: Heightened amygdala reactivity and event-related responses to positive social stimuli in Williams syndrome. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(4), 1132-9. PubMed
Järvinen-Pasley, A., Bellugi, U., Reilly, J., Mills, D.L. Galaburda, A, Reiss, A.L., & Korenberg, J.R. (2008). Defining the social phenotype in Williams syndrome: A model of linking gene, the brain, and cognition. Development and Psychopathology, 20(1), 1-35. PubMed
Gothelf, D., Searcy, Y. M., Reilly, J., Lai, P.T., Lanre-Amos, T., Mills, D., Korenberg, J., Galaburda, A., Bellugi, U., & Reiss, A. (2008). Association between cerebral shape and social use of language in Williams syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 146A(21), 2753-2761. PubMed
Zitzer-Comfort, C., Doyle, T., Masataka, N., Korenberg, J., & Bellugi, U. (2007). Nature and Nurture: Williams syndrome across cultures. Developmental Science, 10(6), 755-62. PubMed
Reilly, J., Losh, M., Bellugi, U., Wulfeck, B. (2004). “Frog, where are you?” Narratives in children with specific language impairment, early focal brain injury, and Williams syndrome. Brain and language, 88(2):229-47. PubMed
Doyle, T.F., Bellugi, U., Korenberg, J.R. & Graham, J. (2004). “Everybody in the world is my friend”: Hypersociability in young children with Williams Syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 124A(3), 263-273. PubMed
Losh, M., Bellugi, U., Reilly, J., Anderson, D. (2000). Narrative as a Social Engagement Tool: The Excessive Use of Evaluation in Narratives from Children with Williams Syndrome. Narrative Inquiry. 10(2), 265-290. Link
Press Releases
Neurodevelopmental Model of Williams Syndrome Offers Insight into Human Social Brain (2016) Salk News Link to article
Women & Science events entertain and inspire (2016) Inside Salk Link to article
Three Salk faculty honored as recipients of senior scientist chair (2015) Inside Salk Link to article
Salk Institute Founders’ Chair, Ursula Bellugi (2015) Link to article
Connecting the Dots between Genes and Human Behavior (2014). Salk News Link to article
Women & Science lecture gives glimpse of how scientists are using stem cells to model autism spectrum disorder (2014) Inside Salk Link to article
NIH Awards Salk Institute $5.5 Million Grant to Study Williams Syndrome (2011). Salk News Link to article
Language as a Window to Sociability (2010) Salk News Link to article
The Gregarious Gene? “Everybody in the world is my friend” (2009). Salk News Link to article
Beyond Nature vs Nurture: WS (2007) Link to article
Four of the Nation’s Preeminent Research Institutions Announce Stem Cell Research Alliance (2006). Salk News Link to article
Posters and Other Information
SFN Poster Symposium PPG 2007 [ Link to poster ]
What’s Normal Anyway by Karen Levine [ Link to poster ]
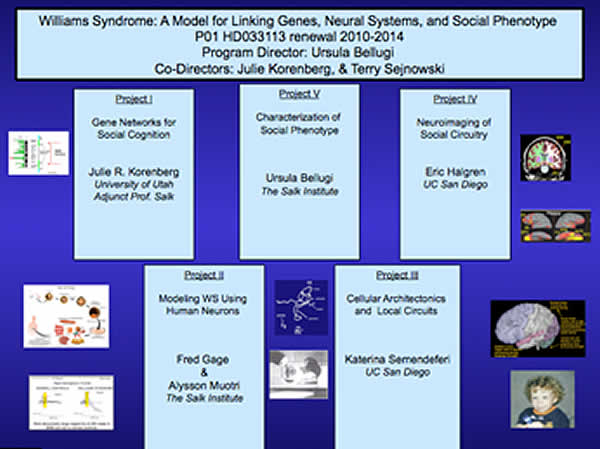
“WILLIAMS SYNDROME: A MODEL FOR LINKING GENES, NEURAL SYSTEMS, AND SOCIAL PHENOTYPE”
P01 NICHD033113 RENEWAL 2010
PROGRAM DIRECTOR: URSULA BELLUGI
CO-PIs: JULIE KORENBERG & TERRY SEJNOWSKI
This exciting proposal is approved for funding ($5,000,000) by NICHD, it builds on a longstanding program project on Williams syndrome to Dr. Ursula Bellugi at the Salk Institute (starting in 1995, renewed in 2000, 2005).
This 2010 renewal has five interrelated projects illuminating gene networks for social cognition, modeling the disorder using human neurons, cellular architectonics, neuroimaging, and social phenotype of Williams syndrome. The research teams are located at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, the University of Utah, and the University of California, San Diego.
This is a unique program project which has made enormous contributions to the study of Williams syndrome. Although the organization has changed over the years, it remains under strong leadership, with Bellugi and contributions from competent investigators to direct the component research projects, recognized leaders in their fields.
Click to read more»
The overarching goal of this application is to link social- affective functions to their underlying neurobiological and molecular genetic bases, using Williams syndrome (WS) as a model. The theme leads from the investigators’ past studies to the hypothesis that genetic and neuropeptide dysregulation underlies the social-affective features of WS. They continue to employ a multi-pronged approach incorporating new techniques and approaches to understanding the neurogenetic systems involved in the WS social phenotype. To this end, Project I: Gene Networks for Social Cognition in WS, determines the role of WS genes in social-emotional behavior using full and atypical deletions; the role of genetic variations for neurotransmitters in WS social-emotional behavior; the expression of WS and neurotransmitter receptor genes in WS brain; and the genetic transcriptional networks altered in WS. Project II: Modeling WS using Human Neurons, models typical and affected human nervous system development in WS using pluripotent stem cells. Studies target genes implicated in social behavior within the WS region for alteration in neuronal development. Project III: Cellular Architectonics and Local Circuits, examines the social brain in WS with newly available technology on a unique collection of WS brains. Project IV: Neuroimaging of Social Circuitry, utilizes new multimodal, integrated structural and functional neuroimaging techniques to test hypotheses about the relationships among brain anatomy, physiology, cognition, and genetics. Project V: Characterization of the Social Phenotype of WS, examines the nature of altered social-affective behavior WS, including the pathways of several “dissociations”, incorporating new technologies and probes for behavior, psychophysiology, and electrophysiology. The results will provide a critical contribution to social neuroscience.
RELEVANCE: A mission of NICHD includes research that leads to increased understanding and treatment of social behavior and emotional disorders. The investigators include research that targets the study of genes, neural circuits, and social behavior in powerful new ways. The results of these studies will provide unprecedented integration of the genetic and brain processes responsible for human social behavior, as well as keys to novel treatments.